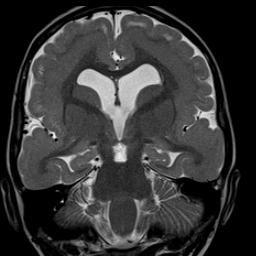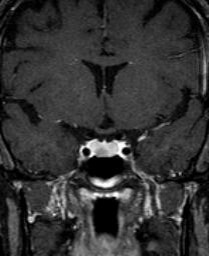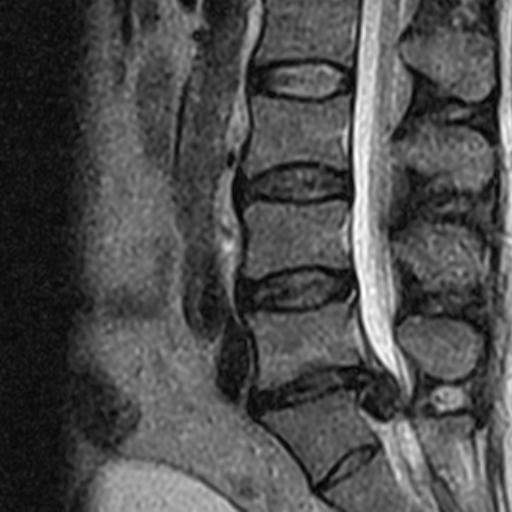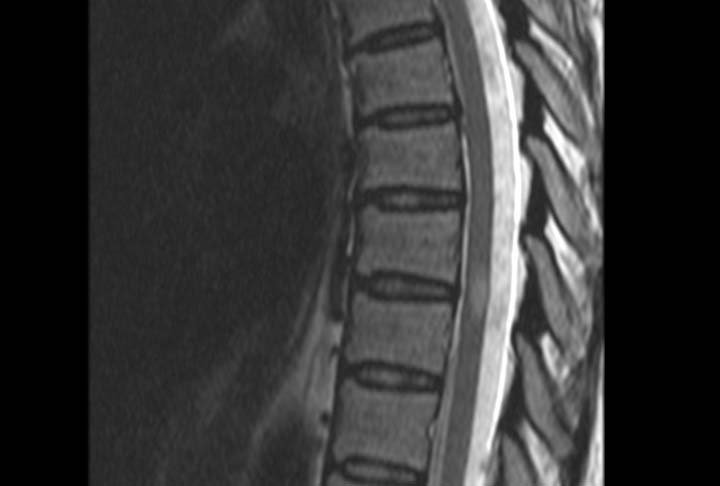
Image 1
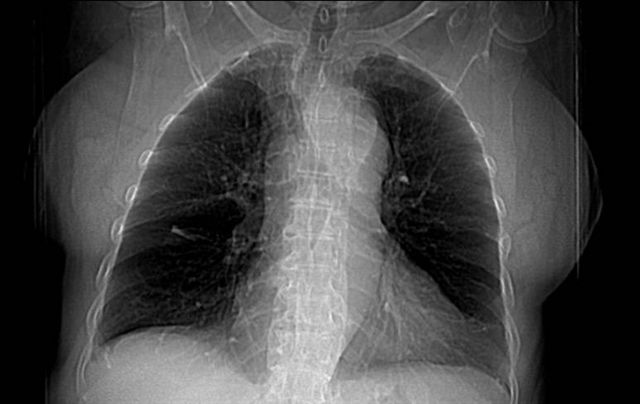
Front view chest x-ray shows prominent aorta
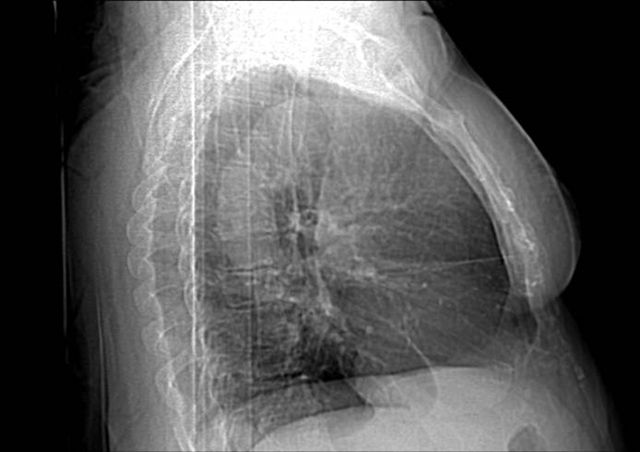
Image 2
Side view chest x-ray shows prominent aorta
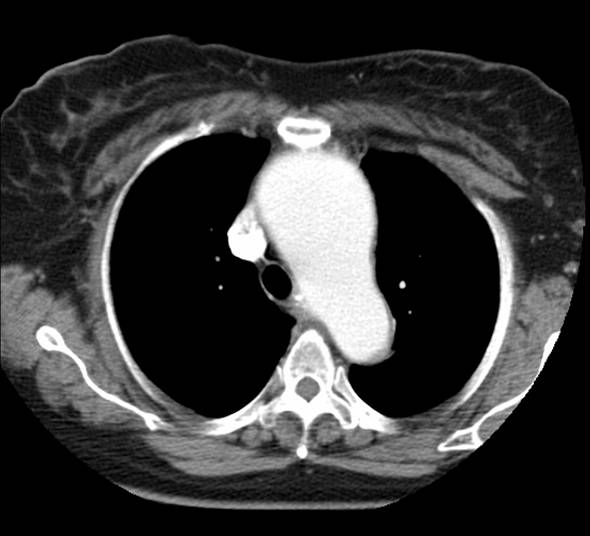
Image 3
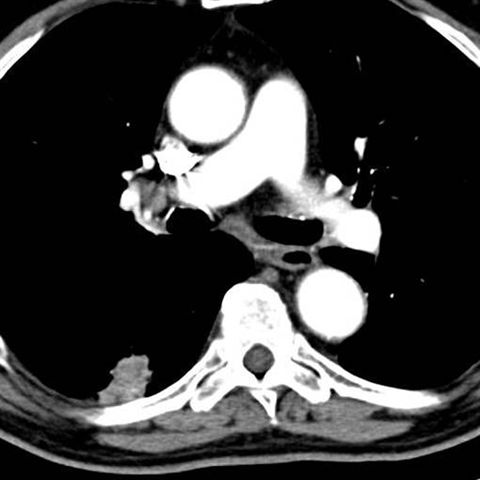
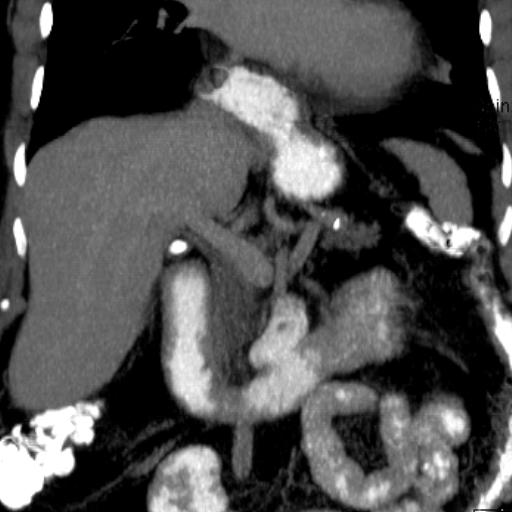
Chest CT with intravenous contrast demonstrates aneurysm of the ascending thoracic aorta correlating with imaging x-rays 1 and 2
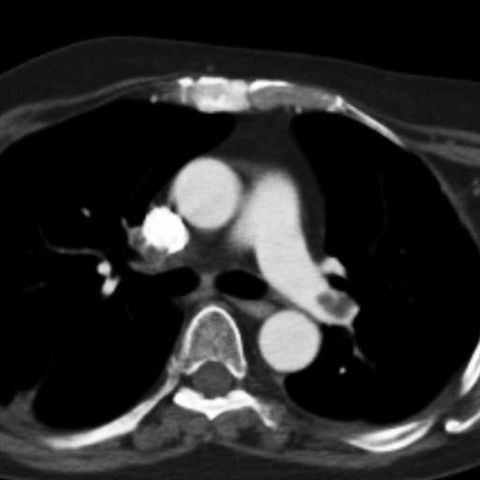
Image 4
Chest CT with intravenous contrast dedicated to the pulmonary arteries demonstrates a filling defect in the left pulmonary artery. This is the typical appearance of a pulmonary embolism. It is mandatory to inject contrast to make this CT diagnosis. The diagnosis is not made with chest x-rays although these are obtained as an initial evaluation
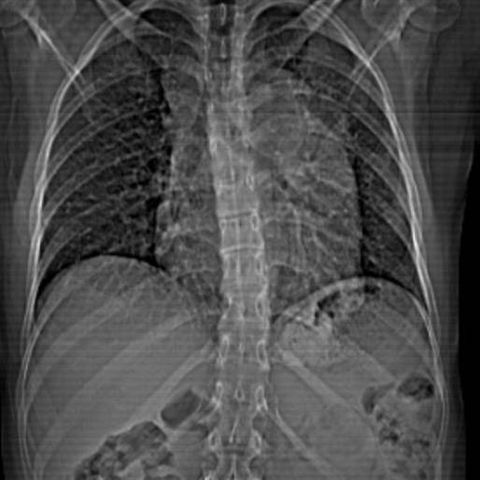
Image 5
Frontal chest x-ray shows abnormally enlarged mediastinum. Chest CT without and with intravenous contrast is indicated to evaluate what produces the X-ray finding
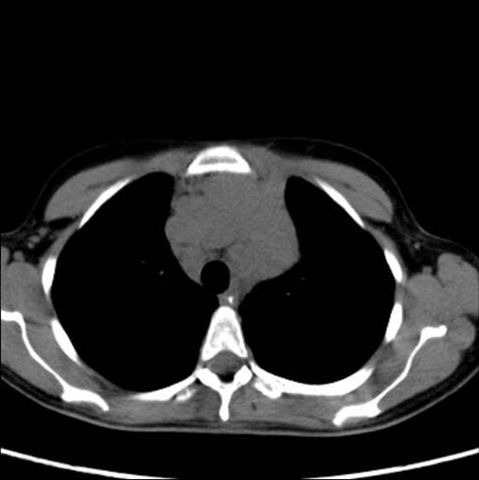
Image 6
Chest CT without intravenous contrast confirms that there is a mass in the mediastinum excluding aortic aneurysm. The non-contrast intravenous image also rules out calcifications in the mass
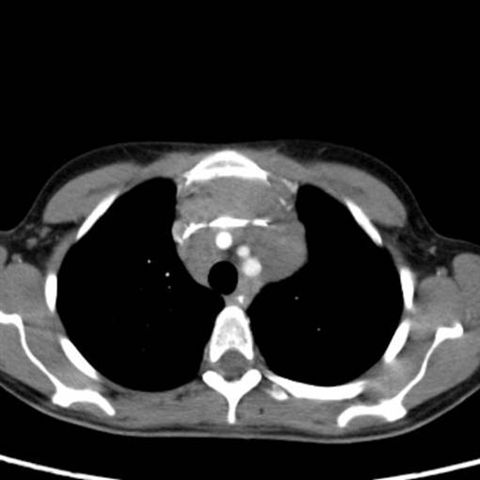
Image 7
Chest CT with intravenous contrast shows that the mass compresses the main arteries in the mediastinum. The mass turned out to be Hodgkin's lymphoma
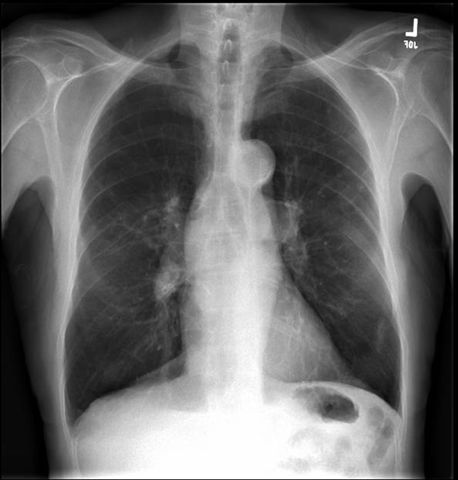
Image 8
Frontal chest x-ray shows emphysema without evidence of mass
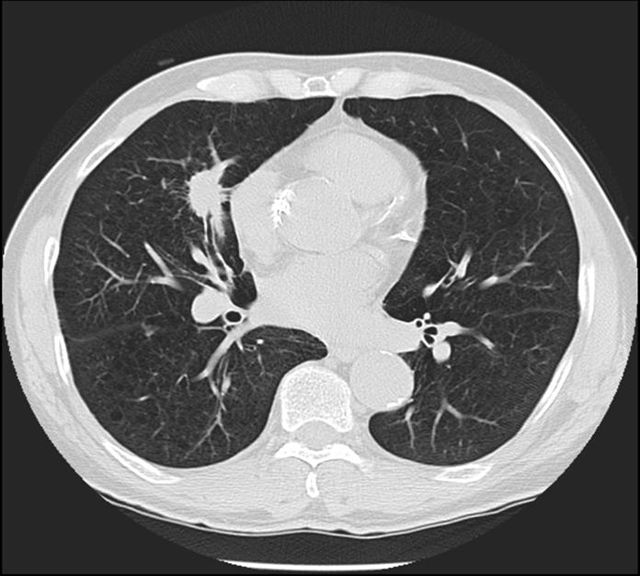
Image 9
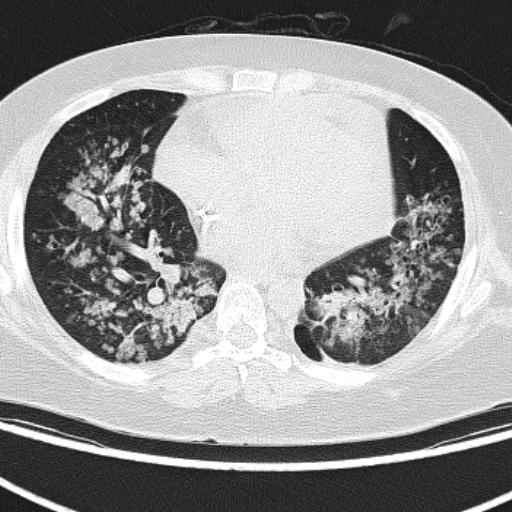
Breast CT shows a non-calcified mass of concern for cancer in the right lung, invisible on x-ray
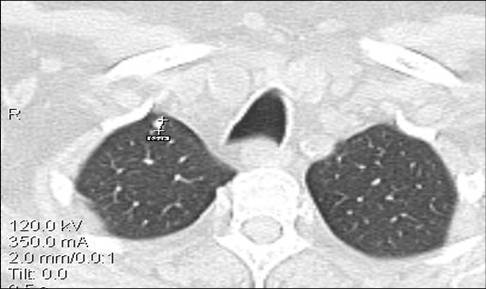
Image 10
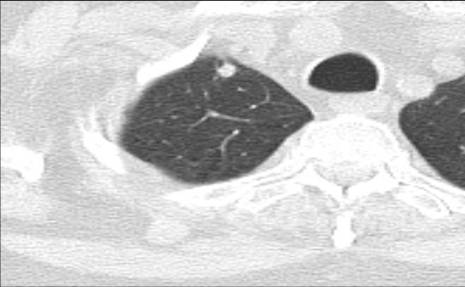
Image 11
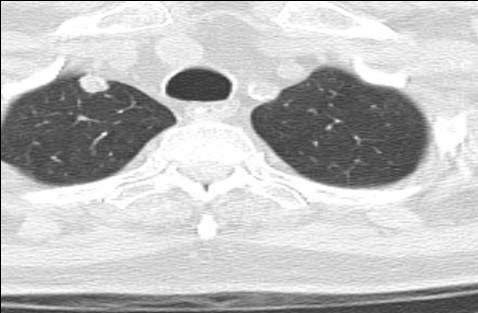
Image 12
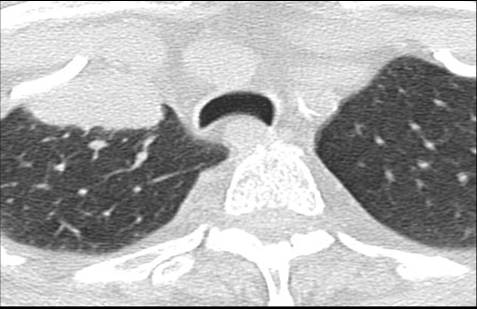
Image 13
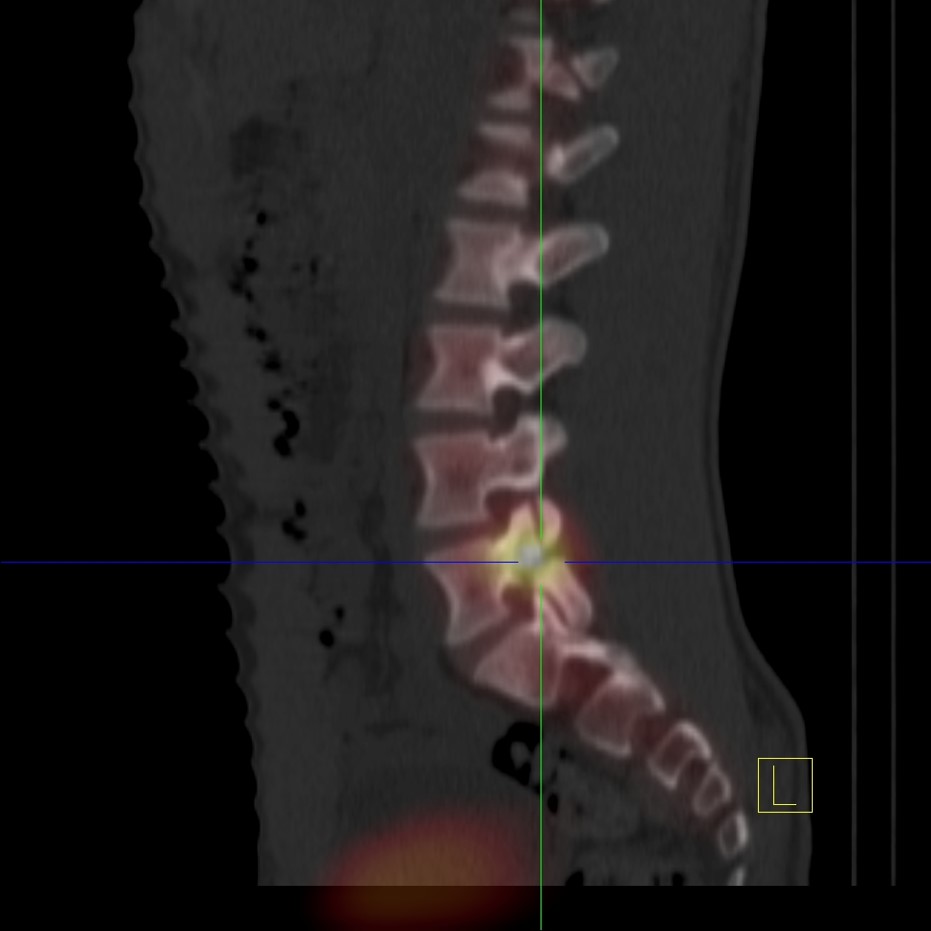
Serial chest CT scans obtained every three months demonstrating the progressive growth of a lung nodule from less than one centimeter to a cancerous mass originating in the right lung and invading the pleura, confirmed by biopsy. From the nodule demonstrating unresponsive growth, a biopsy should be performed as soon as possible to document cancer and determine its cell type. A PET-CT scan from the head to the hips is needed to determine how extensive the disease is (staging)
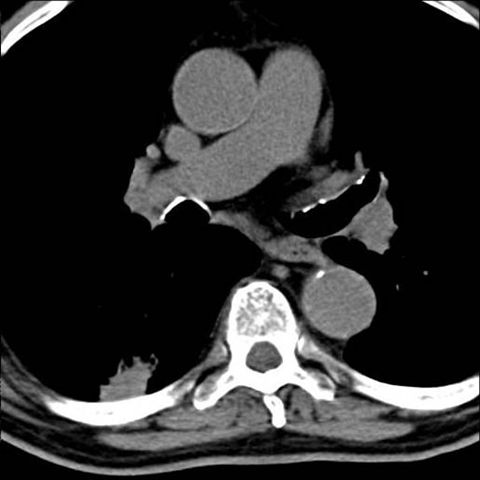
Image 14
Non-contrast intravenous chest CT demonstrates an irregular, non-calcified nodule in contact with the posterior pleura of the right lung